Discovering the Applications of 3D Laser Scanning in Archaeology and Cultural Heritage Conservation
The assimilation of 3D laser scanning modern technology in archaeology and cultural heritage preservation marks a considerable advancement in exactly how archaeological sites and artifacts are documented and examined. This non-invasive method gives specific spatial information, exposing intricate details that were previously challenging to record. As the applications of this technology remain to evolve, different effects for conservation, documents, and education arise, welcoming further exploration into its transformative influence on the area.
Understanding 3D Laser Scanning Innovation
3D laser scanning modern technology has transformed the area of archaeology by supplying accurate and comprehensive spatial data. This sophisticated innovation employs laser beams to catch numerous information factors from a things or website, developing a highly exact three-dimensional depiction (3D Scanning). The resulting factor clouds can expose intricate information of historical sites, structures, and artefacts that may be unseen to the naked eye
Using this technology, archaeologists can document the specific measurements, shapes, and settings of things with unprecedented accuracy. This method decreases the danger of human mistake and removes the requirement for extensive hands-on measurements. In addition, the data accumulated can be assessed and shared conveniently, assisting in partnership amongst scientists. By integrating 3D laser scanning with GIS and other electronic devices, excavators boost their ability to imagine and translate historical contexts, resulting in much deeper insights right into old cultures and settings.
Enhancing Historical Paperwork
3D laser scanning considerably enhances historical documents with its ability to produce exact site maps. This modern technology promotes comprehensive artifact analysis, providing understandings that standard techniques might ignore. In addition, it guarantees the preservation of contextual information, which is crucial for recognizing the partnerships within historical sites.
Exact Website Mapping
While typical mapping techniques typically fight with capturing the detailed details of historical sites, progressed laser scanning innovation uses an advanced approach to precise site mapping. This technique allows archaeologists to develop extremely detailed and accurate three-dimensional representations of sites, showcasing topographical variations and structural functions with remarkable fidelity. The capability to capture numerous information factors in an issue of minutes allows for comprehensive documents, which can be conveniently updated and shared among researchers. Additionally, laser scanning facilitates the measurement of complex geometries that would be challenging to analyze making use of standard devices. Therefore, this innovation enhances the accuracy of site maps, adding considerably to the conservation and understanding of cultural heritage sources.
Thorough Artefact Analysis
Laser scanning innovation substantially improves the analysis of archaeological artefacts, supplying scientists with unprecedented detail and accuracy. This method captures intricate surface appearances, measurements, and includes that typical documents methods might forget. By producing high-resolution 3D models, scholars can closely examine artefacts without the risk of damages inherent in physical handling. This precision permits for better relative researches, enabling professionals to determine manufacturing methods, stylistic variations, and prospective social importance. Moreover, the capability to adjust and imagine data in 3 dimensions assists in a deeper understanding of artefact capability and use. Overall, laser scanning fosters a more complete strategy to archaeological documents, ensuring that vital information regarding artefacts is preserved for future research study and education.
Preservation of Contextual Information
Maintaining contextual data is crucial for enhancing archaeological documents, as it guarantees that searchings for are comprehended within their original ecological and social structures. 3D laser scanning modern technology greatly adds to this preservation initiative by catching detailed spatial partnerships among artefacts, frameworks, and their environments. By creating exact 3D models, archaeologists can document the exact places and positionings of items in situ, promoting a complete understanding of their context. This technology allows scientists to revisit and analyze websites long after excavation, keeping the integrity of contextual information. Furthermore, digital documents developed via scanning can be shared internationally, promoting collective study and public engagement. Eventually, preserving contextual data with 3D laser scanning improves archaeological stories and advertises a more profound admiration of social heritage.
Conservation of Cultural Heritage Sites
As advancements in modern technology remain to evolve, the conservation of cultural heritage websites has actually ended up being significantly reliant on ingenious approaches such as 3D laser scanning. This technology permits the comprehensive paperwork of landscapes, structures, and artifacts, recording their exact measurements and spatial connections in a non-invasive fashion. By developing high-resolution 3D versions, researchers can assess and keep an eye on wear and tear patterns, enabling proactive conservation strategies.
In addition, 3D laser scanning facilitates the sharing of comprehensive site data with the worldwide neighborhood, advertising partnership amongst excavators, preservationists, and historians. These models function as indispensable resources for education and learning and public interaction, elevating recognition of social heritage concerns. In addition, the digital documents developed can guard versus loss as a result of ecological aspects, vandalism, or disregard. In general, 3D laser scanning stands for a transformative technique to the preservation of cultural heritage, guaranteeing that these sites can be studied and valued by future generations.
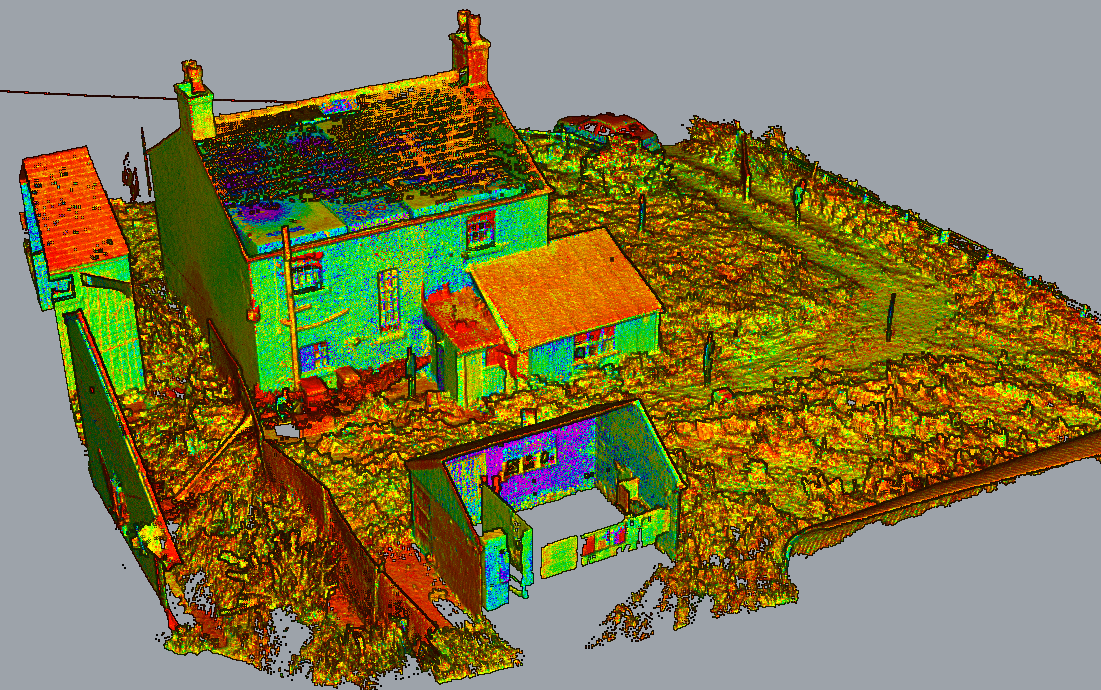
Restoration and Repair Efforts
The in-depth documents accomplished via 3D laser scanning plays a considerable duty in restoration and restoration initiatives within archaeology. This technology supplies more info precise measurements and high-resolution images, allowing for accurate digital versions of artefacts and structures. These versions serve as vital referrals during remediation procedures, enabling archaeologists to envision the initial design and make educated decisions about strategies and products needed for repair service.
Additionally, 3D laser scanning facilitates the repair of damaged or shed components by developing thorough reproductions. This process aids in guaranteeing that restorations preserve historical integrity while also allowing for innovative approaches to bring back sites. The ability to examine wear patterns and structural weaknesses through scanned information boosts understanding of a website's historical context and its usage over time. 3D laser scanning not just preserves the physical facets of social heritage however likewise enriches the story of history, directing future remediation endeavors.
Educational and Study Opportunities
The combination of 3D laser scanning in archaeology opens up substantial academic and research possibilities. Academic collaborations can boost the understanding of old sites, while specialized training workshops outfit experts with vital skills for using this technology. With each other, these initiatives foster a richer interaction with archaeological practices and techniques.
Academic Collaborations in Archaeology
Collaborative efforts in archaeology have ended up being significantly vital for progressing both instructional and study chances. By cultivating partnerships among colleges, research establishments, and cultural heritage organizations, these collaborations assist in the exchange of knowledge and sources, boosting the quality of historical studies. Joint jobs usually leverage varied know-how, enabling ingenious methodologies and detailed analyses, specifically in the application of technologies like 3D laser scanning. Such cooperations additionally promote interdisciplinary methods, involving areas such as history, conservation, and geography science. Additionally, academic partnerships commonly lead to the development of new curricula and training programs, preparing the next generation of archaeologists to efficiently use advanced technologies in their work. Eventually, these alliances add to the conservation and understanding of social heritage.
Educating Workshops for Specialists
Educating workshops for experts in archaeology are progressively important for enhancing abilities in the application of innovative innovations such as 3D laser scanning. These workshops provide participants with hands-on experience in making use of sophisticated tools and software application, promoting a deeper understanding of information capture and analysis processes. Specialists can find out to produce precise digital versions of archaeological sites, which considerably help in paperwork and preservation initiatives. Furthermore, these training sessions typically include conversations on best techniques and study, promoting knowledge exchange amongst participants. By purchasing continuous education, experts can remain upgraded on evolving technologies, ultimately enhancing the effectiveness of their study and cultural heritage conservation initiatives. This commitment to ability enhancement is essential for progressing the area of archaeology.
Future Patterns in 3D Laser Scanning for Archaeology
As innovations in innovation remain to reshape numerous fields, the future of 3D laser scanning in archaeology guarantees to enhance both the precision and effectiveness of website documentation and analysis. Arising trends suggest a growing combination of fabricated intelligence and artificial intelligence, assisting in automated information processing and interpretation. This advancement will certainly allow archaeologists to assess complex datasets faster, leading to faster insights into historical contexts.
Moreover, the combination of drone innovation with 3D laser scanning is most likely to increase, enabling thorough aerial studies of historical sites that are hard to gain access to. The enhancing cost of scanning tools will certainly equalize accessibility, empowering smaller organizations and independent researchers to utilize these devices properly. In addition, advancements in virtual fact and boosted fact will certainly make it possible for immersive experiences for public interaction and education, making historical searchings for a lot more obtainable and interactive. These fads jointly indicate a transformative future for archaeology, enhancing preservation initiatives and expanding the technique's outreach.
Regularly Asked Concerns
Exactly How Much Does 3D Laser Scanning Equipment Cost?

What Are the Limitations of 3D Laser Scanning?
The restrictions of 3D laser scanning include high expenses, possible information processing difficulties, level of sensitivity to environmental conditions, and problem catching complex details in intricate surface areas, which can influence the accuracy and completeness of scanned representations. (3D Scanning)

Can 3D Laser Scanning Be Made Use Of Underwater?
Yes, 3D laser scanning can be used undersea, but it requires customized devices and methods to overcome obstacles such as water distortion and restricted visibility. Effective applications have been shown in aquatic archaeology and underwater surveys.
The length of time Does a Scanning Task Commonly Take?
A scanning job typically takes anywhere from a couple of days to several weeks, relying on the complexity and size of the location being scanned, together with the preparation and post-processing demands associated with the job.
Are There Certain Software Needs for Handling 3D Scans?
Yes, specific software requirements for refining 3D scans consist of programs capable of taking care of huge point clouds, such as Autodesk ReCap, Cyclone, or MeshLab. These devices help with analysis, visualization, and assimilation right into numerous applications successfully.
The combination of 3D laser scanning technology in archaeology and cultural heritage conservation marks a substantial development in just how historical sites and artefacts are documented and assessed. 3D laser scanning technology has changed the field of archaeology by offering specific and detailed spatial information. As improvements in modern technology continue to develop, the conservation of social heritage websites has actually become progressively dependent on innovative methods such as 3D laser scanning. As developments in innovation continue to reshape different areas, the future of 3D laser scanning in archaeology assures to boost both the precision and performance of website documents and evaluation. The assimilation of drone modern technology with 3D laser scanning is most likely to increase, enabling extensive aerial surveys of historical websites that are hard to accessibility.